Marx Lab

Location and Contact Information
Principal Investigator
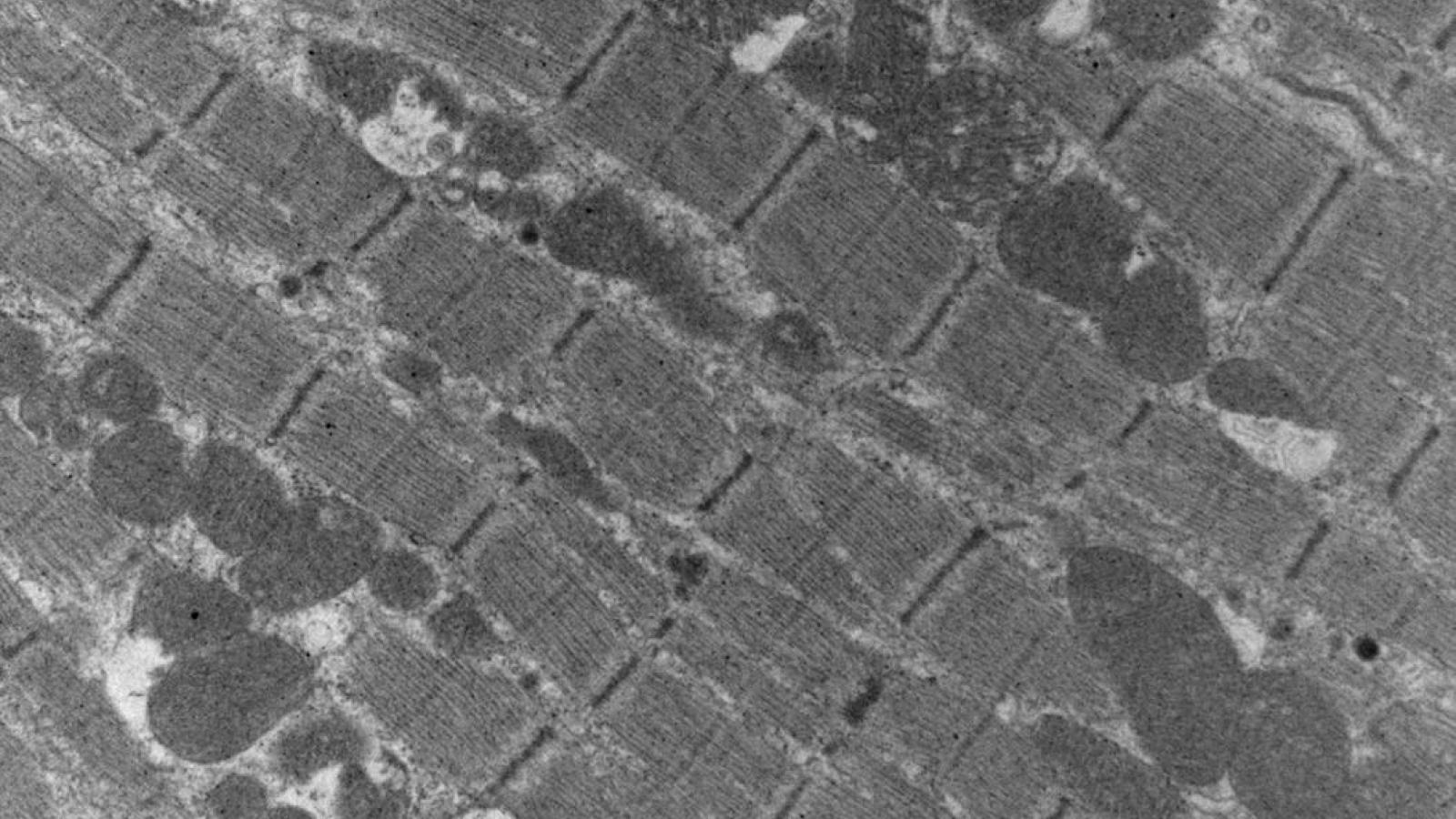
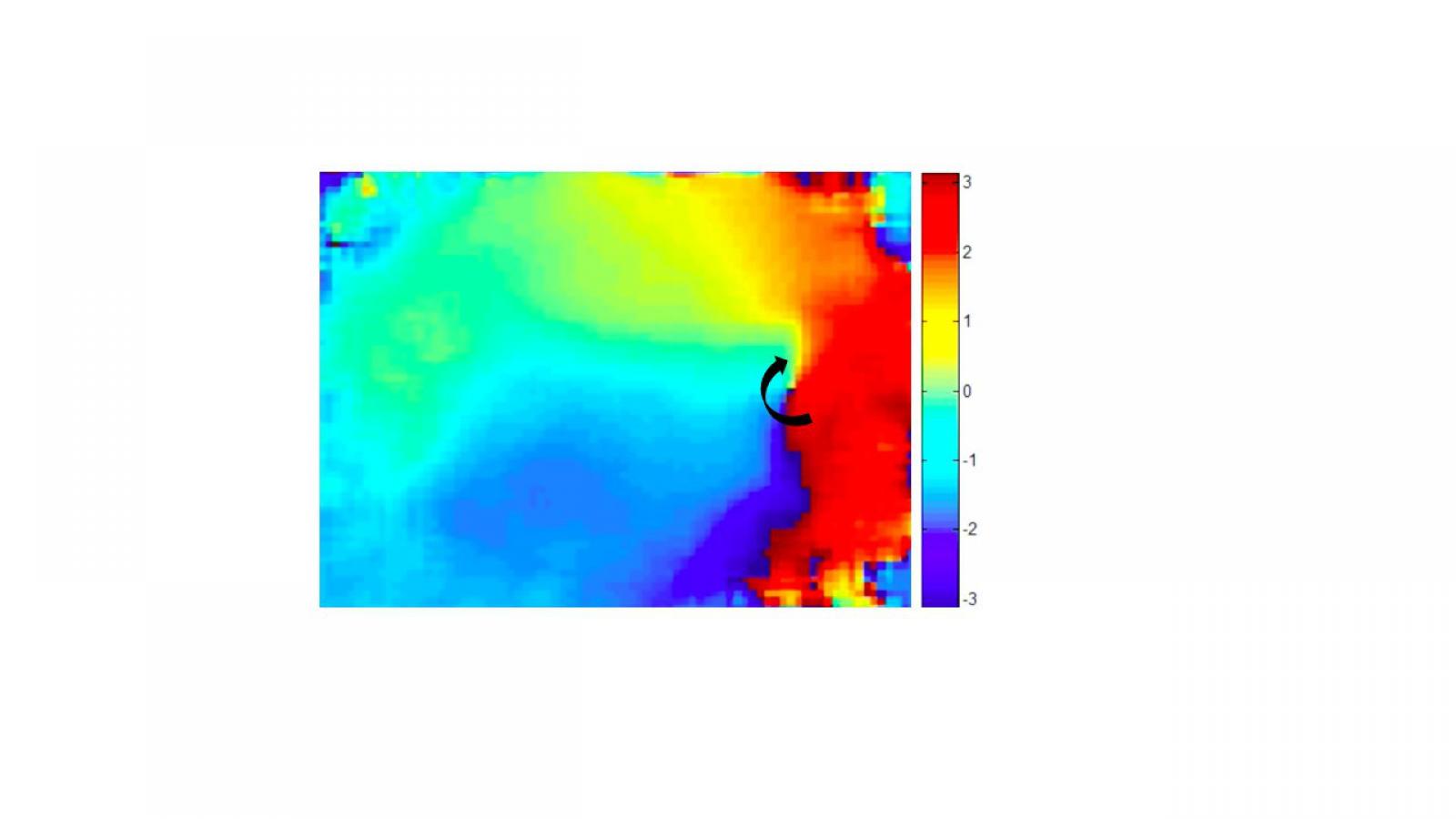
The Marx Lab studies the regulation of ion channels by macromolecular complexes. We have demonstrated that specific sequences within the ion channel (leucine zippers) recruit regulatory proteins, which modulate the ion channel function in normal and pathologic conditions. The laboratory is now focused on understanding the molecular components and functional implications of macromolecular complex formation of the large conductance calcium-activated potassium channel (BKCa, maxi-K) and the L-type voltage gated calcium channel. The laboratory utilizes both molecular biologic and electrophysiologic (planar lipid bilayer, patch clamp) techniques to elucidate these fundamental processes and emphasizes the links between these fundamental molecular processes and systems function. To date our work has had significant impact in understanding the triggers of fatal cardiac arrhythmias and mechanical dysfunction in heart failure. Present experiments are very likely to impact our understanding of control of peripheral blood pressure by the sympathetic nervous system.
The Marx Lab collaborates with the Wan Lab and the Morrow Lab to develop new methods of diagnosing and treating arrhythmias. Our scientists have made major advances in understanding the molecular and cellular bases for and the fundamental mechanisms of complex, life-threatening arrhythmias and sudden cardiac death. Our research program is focused in two major areas:
- Cardiac: studying the regulation of ion channels in normal and pathological conditions in the heart. Altered cardiac ion channel function is associated with heart failure and arrhythmias.
- Vasculature: understanding molecular mechanisms leading to vascular smooth muscle proliferation, migration, and contractility.
Our combined mission is to promote and stimulate interdisciplinary research in the cardiovascular field, with the overall goal of developing new and effective approaches for the diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the heart and blood vessels and the prevention of premature death.
Lab Members
Jared Kushner, MD
- Postdoctoral Clinical Fellow; Assistant in Clinical Medicine
Select Publications
1. Lehnart SE, Huang F, Marx SO, Marks AR.Immunophilins and coupled gating of ryanodine receptors. [Review.] Curr Top Med Chem.
2. Marx S. (2003) Ion channel macromolecular complexes in the heart. [Review.] J Mol Cell Cardiol. 3(12):1383-91.
3. Kass RS, Kurokawa J, Marx SO, Marks AR. (2003) Leucine/isoleucine zipper coordination of ion channel macromolecular signaling complexes in the heart. Roles in inherited arrhythmias. [Review.] Trends Cardiovasc Med. 35(1):37-44.
4. Marx SO, Marks AR. (2003) Regulation of the ryanodine receptor in heart failure. [Review.] Basic Res Cardiol. 13(2):I49-51.
5. Marks AR, Marx SO, Reiken S. (2002) Regulation of ryanodine receptors via macromolecular complexes: a novel role for leucine/isoleucine zippers. [Review.] Trends Cardiovasc Med. 12(4):166-70.
6. Marks AR, Reiken S, Marx SO. (2002) Progression of heart failure: is protein kinase a hyperphosphorylation of the ryanodine receptor a contributing factor? Circulation. 105(3):272-5.